Did you ever wonder what causes that earthy smell that rises after a light summer rain? That mysterious scent has been called “petrichor”, and a main component of it is an organic compound called geosmin, which lingers around moist soil.
Geosmin comes from the ancient Greek “geo”, meaning earth, and “osme”, meaning smell. We use this scent as an ingredient in perfumes and it is what gives beetroot its earthy flavour. Geosmin can also be perceived as an “off” flavour in water and wine.
Animals can detect geosmin. Fruit flies, for example, dislike geosmin and they avoid anything that smells of it, possibly to avoid contaminated and potentially toxic food. But why is geosmin made in the soil? As part of a team of scientists from Sweden, the UK and Hungary, we discovered the fascinating biology behind this enigmatic compound.
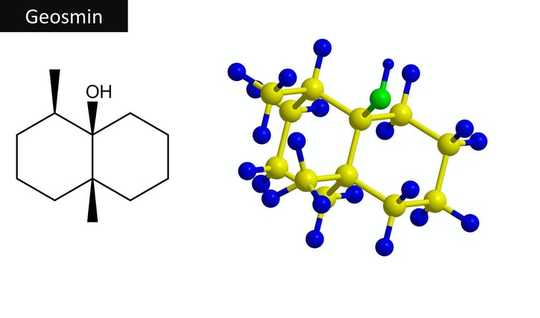 The chemical structure of geosmin. Raimundo79/Shutterstock
The chemical structure of geosmin. Raimundo79/Shutterstock
Get The Latest By Email
Smells like (microbial) team spirit
Scientists have known since the 1960s that geosmin is made by microorganisms in the soil, primarily by bacteria with the scientific name Streptomyces. These bacteria are abundant in soil and are among nature´s best chemists, as they make a wide range of molecules (called specialised metabolites) from which many antibiotics derive. Streptomycetes and their close relatives make thousands of different specialised metabolites – a true treasure trove for the potential discovery of new antibiotics.
It turns out that all streptomycetes have the gene for making geosmin, suggesting that it has an important function. But what do these bacteria gain from producing geosmin? This has been a longstanding mystery.
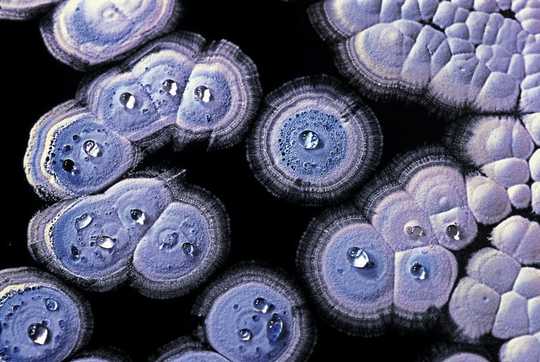 Streptomycete bacteria are commonly found in soil and are famous for being the source of many currently used antibiotics. Tobias Kieser/John Innes Center, Norwich., Author provided
Streptomycete bacteria are commonly found in soil and are famous for being the source of many currently used antibiotics. Tobias Kieser/John Innes Center, Norwich., Author provided
In our recent study, we found that geosmin is part of the chemical language in a mutually beneficial relationship between Streptomyces bacteria and springtails, insect-like organisms that are abundant in the ground.
We discovered this by asking if there could be soil organisms out there that would be attracted to the smell of Streptomyces. We baited traps with colonies of Streptomyces coelicolor and placed them in a field. Our traps captured several types of soil organisms, including spiders and mites. But strikingly, it was springtails that showed a particular preference for the traps baited with geosmin-producing Streptomyces.
Using a particular species of springtail, Folsomia candida, we tested how these creatures sense and react to geosmin. We placed electrodes on their tiny antennae (the average body size of springtail is about 2mm) and detected which smells stimulated them.
 Springtails were tested to see how they react to the odour of geosmin. Béla P. Mólnar/Centre for Agricultural Research, Hungary., Author provided
Springtails were tested to see how they react to the odour of geosmin. Béla P. Mólnar/Centre for Agricultural Research, Hungary., Author provided
Geosmin and the related earthy odorant 2-methylisoborneol were sensed by the antennae, which is essentially the creature’s nose. By studying springtails walking in Y-shaped glass tubes, we saw they had a strong preference for the arm that smelled of these earthy compounds.
The benefit for the animals seems to be that the odours lead them to a source of food. While geosmin-emitting microbes are often toxic to other organisms which avoid them, we found that it did no harm to the springtails we tested.
But how does producing these compounds benefit the bacteria? Streptomycetes normally grow as mycelium – a network of long, branching cells that entwine with the soil they grow in. When they run out of nutrients or conditions in the soil deteriorate, the bacteria escape and spread to new places by making spores that can be spread by wind or water.
Our new finding is that spore production also includes the release of those earthy odorants that are attractive to springtails – and that helps spread the spores by another route.
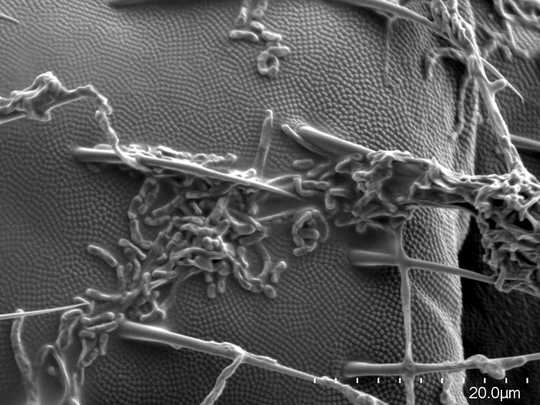 Streptomyces spores cling to the cuticles of a springtail, helping spread the bacteria in the soil. Ola Gustafsson/Lund University, Author provided
Streptomyces spores cling to the cuticles of a springtail, helping spread the bacteria in the soil. Ola Gustafsson/Lund University, Author provided
As the springtails grazed on a Streptomyces colony, we saw spores sticking to their cuticle (the outer surface of the animal). Springtails have a special anti-adhesive and water-repellent surface that bacteria typically don’t stick to, but Streptomyces spores can adhere, probably because they have their own water-repellent surface layer. Spores eaten by the springtails can also survive and be excreted in faecal pellets.
So, springtails help spread Streptomyces spores as they travel through the soil, in much the same way pollinating bees are lured to visit flowers and take with them the pollen grains that adhere to their bodies and fertilise the other plants they visit. Birds eat attractive berries or fruits and help the plant to spread its seeds with their droppings.
Next time you encounter that earthy smell, let it be a reminder of the fascinating and extremely valuable bacteria that thrive in the ground beneath your feet. You might be listening in on an ancient type of communication between bacteria and the creatures that live with them in the soil.![]()
About The Author
Klas Flärdh, Professor of Molecular Cell Biology, Lund University and Paul Becher, Associate professor in Chemical Ecology, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
books_gardening








